After finishing my basics in electronics i wanted to try my hand at programming micro controllers and this post is a direct result of my adventure in learning micro controller programming.
Read on If
STC is a Chinese design company which produces improved derivatives of the classic 8051 MCU. You can get more info from stcmcu.com (in English en.stcmcu.com) or mcu-memory.com. The STC chips seems to be manufactured by a variety of other companies e.g stcmicro.com, stc-51.com, also i see reference to the Taiwanese company tsmc.com, anyway this does not matter to us.
The one i am using is STC89C52RC(why? because that's the one that came with the kit :) )
I think its better to buy a development board with the latest MCU i.e the 90, 10, 11, 12 or 15 series as it has English software and manual.
BTW stc-51.com is selling development boards(starter kit at 25 USD) with the STC12C5A60S2 chip which has the English programming tool(STC ISP V4.86)
Terminology used below:
Things you need:
A development board is a circuit board which holds the MCU and has other components to test the MCU. The components may be other IC or discrete ones like LEDs, buttons, relays etc., For us this is the target board.
I got a development board (STC Kit) which also supports programming through serial interface.
A compiler is a software which convert your human readable program into machine language which the machine(microprocessor within the computer) can understand.
A cross compiler is a compiler which generates the machine code in a format different from the processor it is running on e.g. it runs on your PC and generates code for MCU and the architecture of the microprocessor in you PC(x86) is different from the MCU(8051). The destination architecture is called the target.
Read on If
- You are a newbie to micro controllers and want to learn the easiest way to program i.e. don't want to solder circuits, don't want to learn internals of micro controller(yet) etc.,
- You are ready to spend 30 to 40 CAD
- If you don't know Chinese(because the micro controller i am using 'STC' is a Chinese made one and has better information in Chinese)
- You are ok to do some C coding.
STC is a Chinese design company which produces improved derivatives of the classic 8051 MCU. You can get more info from stcmcu.com (in English en.stcmcu.com) or mcu-memory.com. The STC chips seems to be manufactured by a variety of other companies e.g stcmicro.com, stc-51.com, also i see reference to the Taiwanese company tsmc.com, anyway this does not matter to us.
The one i am using is STC89C52RC(why? because that's the one that came with the kit :) )
I think its better to buy a development board with the latest MCU i.e the 90, 10, 11, 12 or 15 series as it has English software and manual.
BTW stc-51.com is selling development boards(starter kit at 25 USD) with the STC12C5A60S2 chip which has the English programming tool(STC ISP V4.86)
Terminology used below:
| MCU | Microcontroller Unit | |
| IDE | Integrate Development Environment | A graphical development tool which combines a editor, compiler, linker etc., |
| ISP | In System Programming | A way to load user program into MCU without removing the MCU from the target system |
| ICSP | In Circuit Serial Programming | A subset of ISP |
| IC | Integrate Circuit |
Things you need:
- A MCU development board
- A cross compiler
- A Programmer
A development board is a circuit board which holds the MCU and has other components to test the MCU. The components may be other IC or discrete ones like LEDs, buttons, relays etc., For us this is the target board.
I got a development board (STC Kit) which also supports programming through serial interface.
It cost me about 30 CAD and comes with everything you need to start writing programs for MCU and to test your programs.The only snag here is that everything is in Chinese !!! I had to use Google to translate to English. I have provided the details of all that i have learnt through this process.
STC Development board
Closeup of the MCU (This is a 40 pin DIP - Dual Inline Package)
Cross compiler:STC Development board
Closeup of the MCU (This is a 40 pin DIP - Dual Inline Package)
A compiler is a software which convert your human readable program into machine language which the machine(microprocessor within the computer) can understand.
A cross compiler is a compiler which generates the machine code in a format different from the processor it is running on e.g. it runs on your PC and generates code for MCU and the architecture of the microprocessor in you PC(x86) is different from the MCU(8051). The destination architecture is called the target.
One good cross compiler is Keil. You can download a demo copy of Keil from https://www.keil.com/c51/demo/eval/c51.htm. This has the µVision IDE and C51 compiler for writing and compiling C program. Although the demo has limitation on the size of binary generated etc., this is enough for starter.
Note: There are other commercial and open source compiler and IDE which you can use for 8051.
Keil also provides a lot of sample programs for 8051, refer http://www.keil.com/download/list/c51.htm
You can also use an assembler e.g. A51 from Keil or BASIC e.g BASCOM if you are comfortable or familiar with those.
The Real Stuff:
At this point if you have got the stuff 1 &2 from 'Things you need' you are ready for setup and then to write your first program. Below are the steps you should follow
Click on INSTALL
After installing the driver connect the USB to Serial cable to your PC using the USB port.
Windows will prompt you to install driver for the new hardware, chose windows to automatically install the driver.
After successful configuration, verify that the driver has been installed properly using the device manager. You should be seeing a new COM port(e.g COM4) assigned. The port assignment is based on the USB port you connect the cable to.
If you unplug the cable, the device manager will refresh as below
Unfortunately i am unable to find the English version of the tool which supports STC89C52RC (i guess its better to buy a development board with the latest MCU i.e the 90, 10, 11, 12 or 15 series).
I downloaded a later version (4.83) from stcmcu.com and installed it
Step 4: Setup and test hardware
Now connect the development board to your PC and switch on the power
You should see the factory loaded program running. :) The board is working !!!
Don't worry if nothing happens, power off and recheck the connections. If still nothing happens, maybe there is no pre-installed program, just carry on.
Now to program the MCU you need to connect the serial cable. Power off the board and connect the USB to Serial cable. Switch on the power and you should see the existing program running again.
Hardware setup and testing is complete
Step 5: Write a simple program in C using Keil
All the best.
External Links:
- Atmel Studio 6 (free) http://www.atmel.com/microsite/atmel_studio6/
- Microchip MPLab X (demo) http://www.microchip.com/pagehandler/en-us/family/mplabx/
- SDCC (opensource) http://sdcc.sourceforge.net/
- GCC (opensource) http://gcc.gnu.org/install/binaries.html
- MicroElektronika (demo 2k limit) http://www.mikroe.com/mikroc/8051/
Keil also provides a lot of sample programs for 8051, refer http://www.keil.com/download/list/c51.htm
You can also use an assembler e.g. A51 from Keil or BASIC e.g BASCOM if you are comfortable or familiar with those.
Programmer:
A tool to transfer the machine code to the MCU
A programmer consist of a software part and/or a hardware part. The above development boards supports programming using serial port and comes with a USB to serial adapter cable(more on this later)
A tool to transfer the machine code to the MCU
A programmer consist of a software part and/or a hardware part. The above development boards supports programming using serial port and comes with a USB to serial adapter cable(more on this later)
The accompanying CD comes with a programing software(STC ISP V4.80)
If you are buying a universal programmer make sure it supports
the MCU in the development board and also has a good user manual in the language you understand.
BTW most of the MCU nowadays support ISP so you can buy a USB ISP tool and wire it to the ISP pins on the MCU or to the ISP port on the development board.
The Real Stuff:
Step 1: Install the USB to Serial driver
This is needed to download your program into the MCU
Install the driver (HL-340) from the CD or google for HL-340 driver
This is needed to download your program into the MCU
Install the driver (HL-340) from the CD or google for HL-340 driver
Click on INSTALL
After installing the driver connect the USB to Serial cable to your PC using the USB port.
Windows will prompt you to install driver for the new hardware, chose windows to automatically install the driver.
After successful configuration, verify that the driver has been installed properly using the device manager. You should be seeing a new COM port(e.g COM4) assigned. The port assignment is based on the USB port you connect the cable to.
If you unplug the cable, the device manager will refresh as below
How to open device manager in XP ? Simple, type devmgmt.msc in the Run dialog box(Win key + r)
Closeup of the USB to RS-232 chip inside the cable
Closeup of the USB to RS-232 chip inside the cable
Keil has a device database which is used to select a specific target MCU for your program. STC is not available by default but fortunately STCMCU has provided the device database file for Keil. Refer to stcmcu.com for getting the CDB file or download it from STC Artifact
To add STC MCU to Keil device DB:
To add STC MCU to Keil device DB:
Based on your version of Keil (uv2, uv3 or uv4), copy the corresponding CDB to kiel install and update the tools.ini file as below
For e.g. if you have µVision 4 installed in c:\keil
1. Copy uv4.cdb to c:\keil\uv4\uv4.stc.cdb
2. Update c:\keil\tools.ini as follows
[uv2]
CDB0=uv4\uv4.stc.cdb ("STC")
Now when you list the devices available in Keil(File->Device Database) you can see two groups, "Generic CPU" and STC
All the STC MCUs are under the STC grouping
Now when you list the devices available in Keil(File->Device Database) you can see two groups, "Generic CPU" and STC
All the STC MCUs are under the STC grouping
Adding STC specific registers(optional):
STC has its own set of SFR(Special Function Registers), these are defined in the STC header file, refer to STCMCU.com or STC Artifact
Step 3: Install the program download tool(stc-isp-v4.80)
Unfortunately i am unable to find the English version of the tool which supports STC89C52RC (i guess its better to buy a development board with the latest MCU i.e the 90, 10, 11, 12 or 15 series).
I downloaded a later version (4.83) from stcmcu.com and installed it
Step 4: Setup and test hardware
Now connect the development board to your PC and switch on the power
You should see the factory loaded program running. :) The board is working !!!
Don't worry if nothing happens, power off and recheck the connections. If still nothing happens, maybe there is no pre-installed program, just carry on.
Now to program the MCU you need to connect the serial cable. Power off the board and connect the USB to Serial cable. Switch on the power and you should see the existing program running again.
Hardware setup and testing is complete
Step 5: Write a simple program in C using Keil
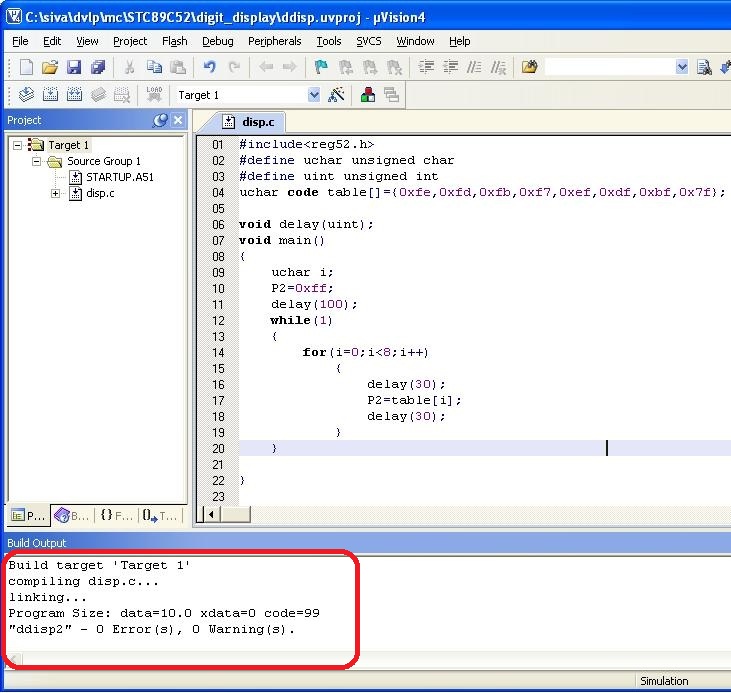
Startup Keil, create a new project and select the target as STC89C52RC(or the MCU you are using). Create a C source file and add it to the project. Google on how to use Keil.
I just copied some code from the CD that came with the board, this displays numbers in the first 7 segment LED display
You should not see any errors in the build output window
If you see some error fix them like you fix any C compiler error
After fixing all the errors now its time to generate .hex file (The hex file is the binary file which is loaded into the MCU, google "hex file format" for more info)
Configure output to generate .hex file
If you see some error fix them like you fix any C compiler error
After fixing all the errors now its time to generate .hex file (The hex file is the binary file which is loaded into the MCU, google "hex file format" for more info)
Configure output to generate .hex file
Step 6: Download the hex file into the MCU
Turn off the MCU board
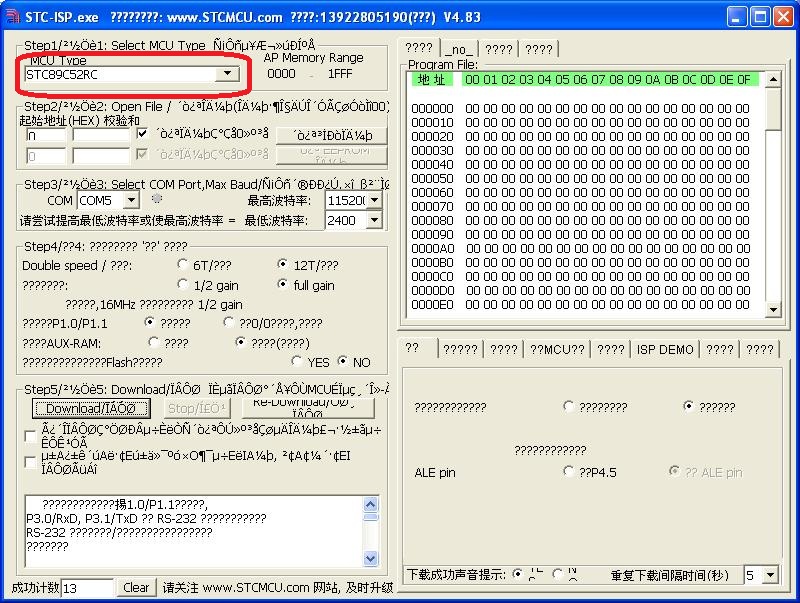
Start the STC-ISP software(double click STC_ISP_V483.exe)
Select the target MCU
Turn off the MCU board
Start the STC-ISP software(double click STC_ISP_V483.exe)
Select the target MCU
Open the hex file
Configure the COM port (1), this is the port displayed in device manager when you connected the USB to Serial cable. Note: The green dot would light up if the correct COM port is selected.
Select download (2)
You should see the programmer waiting (3)
Now power on the development board
You should see the program getting downloaded
Configure the COM port (1), this is the port displayed in device manager when you connected the USB to Serial cable. Note: The green dot would light up if the correct COM port is selected.
Select download (2)
You should see the programmer waiting (3)
Now power on the development board
You should see the program getting downloaded
If all goes well you should see the 7 segment LED display light up.
Hurray!!! You have just finished programming a MCU.
Although the above blog helps you in setting up and testing programming a MCU you should read more on
1. Basic Electronics
2. Digital Electronics
3. Writing optimized C code
4. MCU architecture
5. Using the MCU outside a development board.
Hurray!!! You have just finished programming a MCU.
Although the above blog helps you in setting up and testing programming a MCU you should read more on
1. Basic Electronics
2. Digital Electronics
3. Writing optimized C code
4. MCU architecture
5. Using the MCU outside a development board.
All the best.
External Links:
Stuff i found related to STC
http://ncrmnt.org/wp/2012/10/01/stcdude-0-1-rc1-is-here/
https://github.com/nekromant/stcdude
If you don't find the STC kit in ebay using the link, search for "STK16 / STK32 STC ATMEL AVR Atmega16 Development Experiment Board MCU AVR"
https://github.com/nekromant/stcdude
If you don't find the STC kit in ebay using the link, search for "STK16 / STK32 STC ATMEL AVR Atmega16 Development Experiment Board MCU AVR"